Hi,
You must use Pytorch’s forward hook to fetch intermediate output from specific layers. Torchdistill provides an easy-to-use wrapper for forward / backward hooks, so you may use these. Unfortunately, I could not simply install through pip install torchdistill due to the requirements, so I just scrapped the code snippet from their repository. You can also refer to this jupyter notebook provided in their repo.
Please try the code below:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
import torchvision
from torchvision import models
from torchvision import transforms
# codes from https://github.com/yoshitomo-matsubara/torchdistill
def get_module(root_module, module_path):
module_names = module_path.split('.')
module = root_module
for module_name in module_names:
if not hasattr(module, module_name):
if isinstance(module, (DataParallel, DistributedDataParallel)):
module = module.module
if not hasattr(module, module_name):
if isinstance(module, Sequential) and module_name.lstrip('-').isnumeric():
module = module[int(module_name)]
else:
logger.info('`{}` of `{}` could not be reached in `{}`'.format(module_name, module_path,
type(root_module).__name__))
else:
module = getattr(module, module_name)
elif isinstance(module, (Sequential, ModuleList)) and module_name.lstrip('-').isnumeric():
module = module[int(module_name)]
else:
logger.info('`{}` of `{}` could not be reached in `{}`'.format(module_name, module_path,
type(root_module).__name__))
return None
else:
module = getattr(module, module_name)
return module
def get_hierarchized_dict(module_paths):
children_dict = OrderedDict()
for module_path in module_paths:
elements = module_path.split('.')
if elements[0] not in children_dict and len(elements) == 1:
children_dict[elements[0]] = module_path
continue
elif elements[0] not in children_dict:
children_dict[elements[0]] = list()
children_dict[elements[0]].append('.'.join(elements[1:]))
for key in children_dict.keys():
value = children_dict[key]
if isinstance(value, list) and len(value) > 1:
children_dict[key] = get_hierarchized_dict(value)
return children_dict
def get_device_index(data):
if isinstance(data, torch.Tensor):
device = data.device
return 'cpu' if device.type == 'cpu' else device.index
elif isinstance(data, abc.Mapping):
for key, data in data.items():
result = get_device_index(data)
if result is not None:
return result
elif isinstance(data, tuple):
for d in data:
result = get_device_index(d)
if result is not None:
return result
elif isinstance(data, abc.Sequence) and not isinstance(data, string_classes):
for d in data:
result = get_device_index(d)
if result is not None:
return result
return None
def register_forward_hook_with_dict(module, module_path, requires_input, requires_output, io_dict):
io_dict[module_path] = dict()
def forward_hook4input(self, func_input, func_output):
if isinstance(func_input, tuple) and len(func_input) == 1:
func_input = func_input[0]
device_index = get_device_index(func_output)
sub_io_dict = io_dict[module_path]
if 'input' not in sub_io_dict:
sub_io_dict['input'] = dict()
sub_io_dict['input'][device_index] = func_input
def forward_hook4output(self, func_input, func_output):
if isinstance(func_output, tuple) and len(func_output) == 1:
func_output = func_output[0]
device_index = get_device_index(func_output)
sub_io_dict = io_dict[module_path]
if 'output' not in sub_io_dict:
sub_io_dict['output'] = dict()
sub_io_dict['output'][device_index] = func_output
def forward_hook4io(self, func_input, func_output):
if isinstance(func_input, tuple) and len(func_input) == 1:
func_input = func_input[0]
if isinstance(func_output, tuple) and len(func_output) == 1:
func_output = func_output[0]
device_index = get_device_index(func_output)
sub_io_dict = io_dict[module_path]
if 'input' not in sub_io_dict:
sub_io_dict['input'] = dict()
if 'output' not in sub_io_dict:
sub_io_dict['output'] = dict()
sub_io_dict['input'][device_index] = func_input
sub_io_dict['output'][device_index] = func_output
if requires_input and not requires_output:
return module.register_forward_hook(forward_hook4input)
elif not requires_input and requires_output:
return module.register_forward_hook(forward_hook4output)
elif requires_input and requires_output:
return module.register_forward_hook(forward_hook4io)
raise ValueError('Either requires_input or requires_output should be True')
class ForwardHookManager(object):
def __init__(self, target_device):
self.target_device = torch.device(target_device) if isinstance(target_device, str) else target_device
self.uses_cuda = self.target_device.type == 'cuda'
self.io_dict = dict()
self.hook_list = list()
def add_hook(self, module, module_path, requires_input=True, requires_output=True):
sub_module = get_module(module, module_path)
handle = \
register_forward_hook_with_dict(sub_module, module_path, requires_input, requires_output, self.io_dict)
self.hook_list.append((module_path, handle))
def pop_io_dict(self):
gathered_io_dict = dict()
for module_path, module_io_dict in self.io_dict.items():
gathered_io_dict[module_path] = dict()
for io_type in list(module_io_dict.keys()):
sub_dict = module_io_dict.pop(io_type)
values = [sub_dict[key] for key in sorted(sub_dict.keys())]
gathered_obj = gather(values, self.target_device) if self.uses_cuda and len(values) > 1 else values[-1]
gathered_io_dict[module_path][io_type] = gathered_obj
return gathered_io_dict
def pop_io_dict_from_device(self, device):
device_io_dict = dict()
device_key = device.index if device.type == 'cuda' else device.type
for module_path, module_io_dict in self.io_dict.items():
device_io_dict[module_path] = dict()
for io_type in list(module_io_dict.keys()):
sub_dict = module_io_dict[io_type]
device_io_dict[module_path][io_type] = sub_dict.pop(device_key)
return device_io_dict
def change_target_device(self, target_device):
if self.target_device.type != target_device.type:
for sub_dict in self.io_dict.values():
sub_dict.clear()
self.target_device = target_device
def clear(self):
self.io_dict.clear()
for _, handle in self.hook_list:
handle.remove()
self.hook_list.clear()
# prepare dataset: We'll use CIFAR-10 as an example
trf = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224,224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
])
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False, transform=trf)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=False)
loader = iter(dataloader)
# device
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available else "cpu")
# fetch model: let's use ResNet18
model = models.resnet18(pretrained=False).to(device)
model.eval()
# attach forward hooks
forward_hook_manager = ForwardHookManager(device)
forward_hook_manager.add_hook(model, 'layer1.0.conv1', requires_input=True, requires_output=False)
forward_hook_manager.add_hook(model, 'layer2.0.conv1', requires_input=True, requires_output=False)
forward_hook_manager.add_hook(model, 'layer3.0.conv1', requires_input=True, requires_output=False)
forward_hook_manager.add_hook(model, 'layer4.0.conv1', requires_input=True, requires_output=False)
# forward pass through ResNet18
x, l = next(loader)
with torch.no_grad():
y = model(x.to(device))
# fetch auxiliary feature maps
io_dict = forward_hook_manager.pop_io_dict()
print(io_dict.keys(), '\n')
# visualize
N = len(io_dict)
fig,ax = plt.subplots(1, N+1, figsize=(5*(N+1), 5))
ax[0].imshow(x.cpu()[0].permute(1,2,0))
ax[0].set_title("Original Image", fontsize=16)
for i, k in enumerate(io_dict.keys()):
feature_maps = io_dict[k]['input']
# average feature maps channel-wise for visualization
feature_maps_avg = feature_maps.squeeze().mean(dim=0, keepdims=True)
feature_maps_avg = feature_maps_avg.cpu().permute(1,2,0)
ax[i+1].imshow(feature_maps_avg)
ax[i+1].set_title(k, fontsize=16)
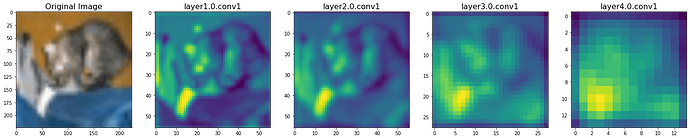
You will get something like below:
Hope this helps!