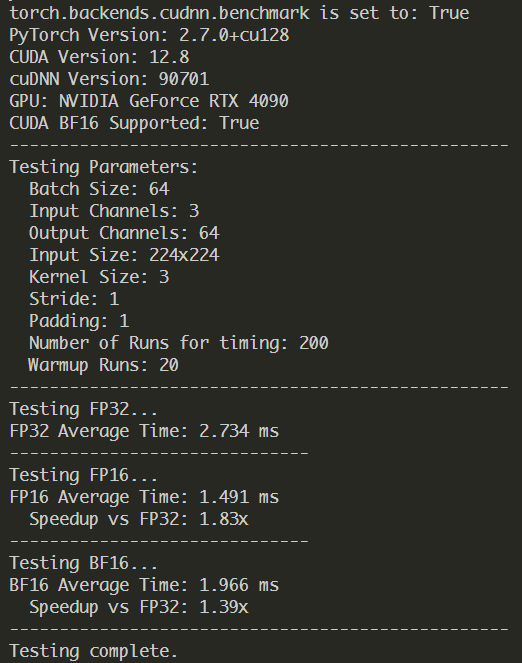
I found that on my nvidia 4090, Conv2d on bfloat16 is always slower than float16. is that an expected behaviour? as i did not find previous cases.
this is my test script, run directly with copy-paste:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import time
# Check if CUDA is available
if not torch.cuda.is_available():
print("CUDA is not available. This script requires a GPU to test BF16/FP16 performance.")
exit()
device = torch.device("cuda")
# Enable cuDNN benchmark mode for potentially faster convolutions
# This should be done after device selection and before model creation if input sizes are fixed.
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
print(f"torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark is set to: {torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark}")
def test_conv_performance(batch_size, in_channels, out_channels, input_size, kernel_size, stride, padding, dtype, num_runs=100, warmup_runs=10):
"""
Tests the performance of a convolutional layer with the specified data type.
Args:
batch_size (int): Input batch size.
in_channels (int): Number of input channels.
out_channels (int): Number of output channels.
input_size (int): Height and width of the input image (assuming square).
kernel_size (int): Size of the convolutional kernel.
stride (int): Stride of the convolution.
padding (int): Padding for the convolution.
dtype (torch.dtype): Data type to test (torch.float32, torch.float16, torch.bfloat16).
num_runs (int): Number of actual test runs.
warmup_runs (int): Number of warmup runs.
Returns:
float: Average execution time per forward pass in milliseconds.
Returns float('nan') if the dtype is not supported.
"""
# Check for data type support on the current GPU
if dtype == torch.bfloat16 and not torch.cuda.is_bf16_supported():
print(f"Warning: BF16 is not supported on this GPU ({torch.cuda.get_device_name(0)}). Skipping BF16 test.")
return float('nan')
# FP16 is generally tested on CUDA
# (Technically, FP16 can run on CPU, but performance benefits are primarily on GPU)
# Create model and input data
try:
model = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding).to(device, dtype=dtype)
# Generate random input tensor on the specified device and with the target dtype
input_tensor = torch.randn(batch_size, in_channels, input_size, input_size, device=device, dtype=dtype)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error creating model or input tensor for {dtype}: {e}")
return float('nan')
# Warm-up GPU: execute the operation a few times before timing
# This helps to ensure that the GPU is in a steady state and any one-time initialization costs are paid.
for _ in range(warmup_runs):
try:
_ = model(input_tensor)
except RuntimeError as e:
# Catch potential runtime errors during warmup, e.g., if a dtype is truly unsupported for an op
print(f"Runtime error during warmup for {dtype} with kernel_size={kernel_size}, padding={padding}: {e}")
# This might indicate an issue with the chosen parameters for this dtype on this hardware
return float('nan')
torch.cuda.synchronize(device=device) # Wait for all CUDA cores to finish warmup operations
# Start timing
# Using torch.cuda.Event for accurate GPU timing
start_event = torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True)
end_event = torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True)
total_time_ms = 0.0
for _ in range(num_runs):
try:
start_event.record()
_ = model(input_tensor)
end_event.record()
torch.cuda.synchronize(device=device) # Ensure the operation is complete for accurate timing
total_time_ms += start_event.elapsed_time(end_event) # elapsed_time returns milliseconds
except RuntimeError as e:
print(f"Runtime error during timed run for {dtype} with kernel_size={kernel_size}, padding={padding}: {e}")
return float('nan')
avg_time_ms = total_time_ms / num_runs
return avg_time_ms
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Define test parameters
batch_size = 64
in_channels = 3
out_channels = 64
input_size = 224 # Common input size, e.g., for ImageNet models
kernel_size = 3
stride = 1
padding = 1
num_runs = 200 # Increase runs for more stable results
warmup_runs = 20 # Sufficient warmup
print(f"PyTorch Version: {torch.__version__}")
if torch.cuda.is_available():
print(f"CUDA Version: {torch.version.cuda}")
print(f"cuDNN Version: {torch.backends.cudnn.version()}")
print(f"GPU: {torch.cuda.get_device_name(0)}")
print(f"CUDA BF16 Supported: {torch.cuda.is_bf16_supported()}")
else:
print("CUDA not available, exiting.")
exit()
print("-" * 50)
print(f"Testing Parameters:")
print(f" Batch Size: {batch_size}")
print(f" Input Channels: {in_channels}")
print(f" Output Channels: {out_channels}")
print(f" Input Size: {input_size}x{input_size}")
print(f" Kernel Size: {kernel_size}")
print(f" Stride: {stride}")
print(f" Padding: {padding}")
print(f" Number of Runs for timing: {num_runs}")
print(f" Warmup Runs: {warmup_runs}")
print("-" * 50)
results = {}
# Test FP32 (Single-precision floating-point)
print("Testing FP32...")
try:
fp32_time = test_conv_performance(batch_size, in_channels, out_channels, input_size, kernel_size, stride, padding, torch.float32, num_runs, warmup_runs)
if not fp32_time != fp32_time: # Check for NaN
print(f"FP32 Average Time: {fp32_time:.3f} ms")
results['fp32'] = fp32_time
else:
print("FP32 test resulted in NaN.")
results['fp32'] = float('nan')
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error during FP32 test: {e}")
results['fp32'] = float('nan')
print("-" * 30)
# Test FP16 (Half-precision floating-point)
print("Testing FP16...")
try:
fp16_time = test_conv_performance(batch_size, in_channels, out_channels, input_size, kernel_size, stride, padding, torch.float16, num_runs, warmup_runs)
if not fp16_time != fp16_time: # Check for NaN
print(f"FP16 Average Time: {fp16_time:.3f} ms")
results['fp16'] = fp16_time
if results.get('fp32') and not results['fp32'] != results['fp32'] and not fp16_time != fp16_time:
print(f" Speedup vs FP32: {results['fp32'] / fp16_time:.2f}x")
else:
print("FP16 test resulted in NaN or was skipped.")
results['fp16'] = float('nan')
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error during FP16 test: {e}")
results['fp16'] = float('nan')
print("-" * 30)
# Test BF16 (BFloat16 floating-point)
print("Testing BF16...")
if torch.cuda.is_bf16_supported():
try:
bf16_time = test_conv_performance(batch_size, in_channels, out_channels, input_size, kernel_size, stride, padding, torch.bfloat16, num_runs, warmup_runs)
if not bf16_time != bf16_time: # Check for NaN
print(f"BF16 Average Time: {bf16_time:.3f} ms")
results['bf16'] = bf16_time
if results.get('fp32') and not results['fp32'] != results['fp32'] and not bf16_time != bf16_time:
print(f" Speedup vs FP32: {results['fp32'] / bf16_time:.2f}x")
else:
print("BF16 test resulted in NaN or was skipped.")
results['bf16'] = float('nan')
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error during BF16 test: {e}")
results['bf16'] = float('nan')
else:
print("BF16 is not supported on this GPU. Skipping test.")
results['bf16'] = float('nan')
print("-" * 50)
print("Testing complete.")
and my output is: