I want to split the dataset into train dataset and valid dataset. but get the error for dataset loader:
class softsensorDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, filepath):
xy = np.loadtxt(filepath, dtype=np.float32, delimiter=',',skiprows=1)
self.len = xy.shape[0]
self.x_data = torch.from_numpy(xy[:,:-1])
self.y_data = torch.from_numpy(xy[:,[-1]])
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.x_data[index], self.y_data[index]
def __len__(self):
return self.len
dataset = softsensorDataset(r"C:\Users\49996\Desktop\coding_vib\softsensor.csv")
train_size = int(len(dataset) * 0.7)
test_size = len(dataset) - train_size
train_loader, test_loader = torch.utils.data.random_split(dataset, [train_size, test_size])
def KL_between_normals(q_distr, p_distr):
mu_q, sigma_q = q_distr
mu_p, sigma_p = p_distr
k = mu_q.size(1)#dimension为1的意思
mu_diff = mu_p - mu_q
mu_diff_sq = torch.mul(mu_diff, mu_diff)#mu_diff的平方
logdet_sigma_q = torch.sum(2 * torch.log(torch.clamp(sigma_q, min=1e-8)), dim=1)
logdet_sigma_p = torch.sum(2 * torch.log(torch.clamp(sigma_p, min=1e-8)), dim=1)
fs = torch.sum(torch.div(sigma_q ** 2, sigma_p ** 2), dim=1) + torch.sum(torch.div(mu_diff_sq, sigma_p ** 2), dim=1)
two_kl = fs - k + logdet_sigma_p - logdet_sigma_q
return two_kl * 0.5
# In[*]
class VIB(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, X_dim, y_dim, dimZ=256, beta=1e-3, num_samples = 30):
# The dimension of Z
super(VIB, self).__init__()
self.beta = beta
self.dimZ = dimZ
self.num_samples = num_samples
# 定义 encoder 从x中生成z,核心参数 mean与std
self.encoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=X_dim, out_features=1024),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=2 * self.dimZ))#和VAE的encoder一致,都要提取出mean和std
# 定义 decoder a simple logistic regression as in the paper
self.decoder_logits = nn.Linear(in_features=self.dimZ, out_features=y_dim)#注意这里和VAE的input,output是不一样的,这里的in是:Z, out是y
#采样先验
def gaussian_noise(self, num_samples, K):
# works with integers as well as tuples
return torch.normal(torch.zeros(*num_samples, K), torch.ones(*num_samples, K)).cuda()# epsilon和Z都是在这里进行采样生成的
#num samples行
#k 列
#P(z)
def sample_prior_Z(self, num_samples):
return self.gaussian_noise(num_samples=num_samples, K=self.dimZ)
#采样过程:就是 mu + sigma*epsilon
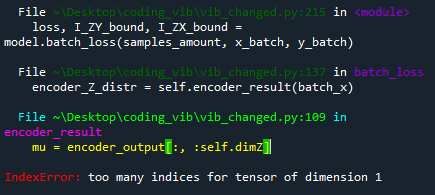
def encoder_result(self, batch):
encoder_output = self.encoder(batch)
mu = encoder_output[:, :self.dimZ]
sigma = torch.nn.functional.softplus(encoder_output[:, self.dimZ:])
return mu, sigma
def sample_encoder_Z(self, num_samples, batch):
batch_size = batch.size()[0]
mu, sigma = self.encoder_result(batch)
return mu + sigma * self.gaussian_noise(num_samples=(num_samples, batch_size), K=self.dimZ)
#前馈就是将x生成z(encoder),与z生成y(decoder)的过程
def forward(self, batch_x):
batch_size = batch_x.size()[0]
# sample from encoder
encoder_Z_distr = self.encoder_result(batch_x) #从batch-x中生成Z
to_decoder = self.sample_encoder_Z(num_samples=self.num_samples, batch=batch_x)
decoder_logits_mean = torch.mean(self.decoder_logits(to_decoder), dim=0)#lower bound L的计算
return decoder_logits_mean
def batch_loss(self, num_samples, batch_x, batch_y):
batch_size = batch_x.size()[0]
#r(z)??
prior_Z_distr = torch.zeros(batch_size, self.dimZ).cuda(), torch.ones(batch_size, self.dimZ).cuda()
#P(z|x_n)
encoder_Z_distr = self.encoder_result(batch_x)
#KL散度部分
I_ZX_bound = torch.mean(KL_between_normals(encoder_Z_distr, prior_Z_distr))
#get z = mean + 0std, samples,均值,方差*采样值 z(todecoder)= mu + sigma * epsilon
to_decoder = self.sample_encoder_Z(num_samples=self.num_samples, batch=batch_x)
# estimated y
decoder_logits = self.decoder_logits(to_decoder)
decoder_logits = decoder_logits.permute(1, 2, 0)
# batch should go first
#def loss
loss = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduce=False, size_average=False)
#reduce为False,则返回每个批处理元素的损失,不进行平均和求和操作
MSE_loss = loss(decoder_logits.permute(2,0,1).squeeze(2), batch_y.unsqueeze(1).expand(batch_y.size()[0], batch_y.size()[1],num_samples).permute(2,0,1).squeeze(2))
#decoder_logits = input
#batch_y[:, None] = target
# estimate E_{eps in N(0, 1)} [log q(y | z)]
MSELoss_montecarlo = torch.mean(MSE_loss, dim=-1)
minusI_ZY_bound = torch.mean(MSELoss_montecarlo, dim=0)
return torch.mean(minusI_ZY_bound + self.beta * I_ZX_bound), -minusI_ZY_bound, I_ZX_bound
# In[*]
beta = 1e-3
batch_size = 100
samples_amount = 30
num_epochs = 10
model = VIB(X_dim=7, y_dim=1, beta = beta, num_samples=samples_amount).cuda()
opt = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.ExponentialLR(opt, gamma=0.97)
# In[*]
import time
i=0
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
loss_by_epoch = []
accuracy_by_epoch = []
I_ZX_bound_by_epoch = []
I_ZY_bound_by_epoch = []
loss_by_epoch_test = []
accuracy_by_epoch_test = []
I_ZX_bound_by_epoch_test = []
I_ZY_bound_by_epoch_test = []
if epoch % 2 == 0 and epoch > 0:
scheduler.step()
#学习率更新
for i, (x_batch, y_batch) in enumerate(train_loader, 0):
x_batch = x_batch.cuda()
y_batch = y_batch.cuda()
loss, I_ZY_bound, I_ZX_bound = model.batch_loss(samples_amount, x_batch, y_batch)
prediction = model.forward(x_batch)
#经过softmax后,选取概率值最大的数值
accuracy = torch.mean(((prediction - y_batch)/y_batch ).float())
loss.backward()
opt.step()
opt.zero_grad()
# compute exponential moving average
I_ZX_bound_by_epoch.append(I_ZX_bound.item())
I_ZY_bound_by_epoch.append(I_ZY_bound.item())
loss_by_epoch.append(loss.item())
accuracy_by_epoch.append(accuracy.item())
for i, (x_batch, y_batch) in enumerate(test_loader, 0):
x_batch = x_batch.cuda()
y_batch = y_batch.cuda()
loss, I_ZY_bound, I_ZX_bound = model.batch_loss(samples_amount, x_batch, y_batch)
logits = model.forward(x_batch)
prediction = torch.max(logits, dim=1)[1]
accuracy = torch.mean(((prediction - y_batch)/y_batch ).float())
I_ZX_bound_by_epoch_test.append(I_ZX_bound.item())
I_ZY_bound_by_epoch_test.append(I_ZY_bound.item())
loss_by_epoch_test.append(loss.item())
accuracy_by_epoch_test.append(accuracy.item())
Thanks for helping me this!