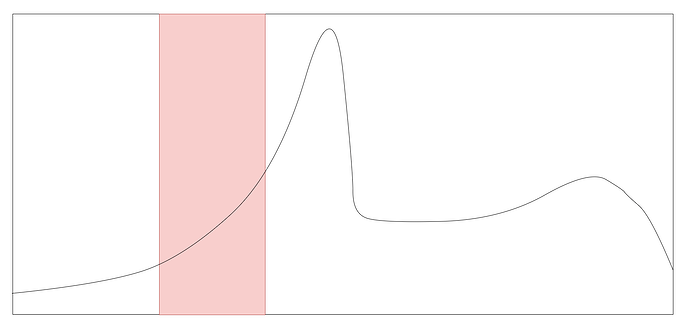
Hey,
I’m trying to do an anomaly detection on an univariate time series with a LSTM autoencoder. E.g. I have a curve like this and the LSTM autoencoder learns everything perfectly except a small part where it seems that it hasn’t learnt anything. In the graph you see the red area which is learnt very bad - maybe you guys have some hints for me that I’m able to improve it?
This is the architecture which I’m using
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.device = get_device()
self.num_features = 1 #Features
self.num_seq_length = 180 #Sequence
self.num_directions = 2 #BiDirectional
self.bidirectional = True if self.num_directions > 1 else False
self.num_hidden_states = 2 #LSTM H,C
self.num_hidden_dim = 16
self.num_enc_hidden_dim = 32 #Dimension
self.num_layers = 3 #Layers
self.dropout = 0.2 #Dropout
self.linear_dims = (self.num_enc_hidden_dim * self.num_directions, 1) #Dimension Linear
self.batch_size = 10
self.lstm_enc1 = nn.LSTM(
input_size=self.num_features,
hidden_size=self.num_hidden_dim,
dropout=self.dropout,
num_layers=self.num_layers,
batch_first=True,
bidirectional=self.bidirectional
)
self.lstm_enc2 = nn.LSTM(
input_size=self.num_hidden_dim*self.num_directions,
hidden_size=self.num_enc_hidden_dim,
dropout=self.dropout,
num_layers=self.num_layers,
batch_first=True,
bidirectional=self.bidirectional
)
self.lstm_enc1.apply(self.init_weights)
self.lstm_enc2.apply(self.init_weights)
def init_weights(self, m):
if type(m) == nn.LSTM:
for name, param in m.named_parameters():
if 'bias' in name:
nn.init.constant(param, 0.01)
elif 'weight' in name:
nn.init.xavier_normal(param) #normal?
def forward(self, x):
batch_size = x.shape[0]
x = x.reshape((batch_size, self.num_seq_length, self.num_features))
x, (hidden, _) = self.lstm_enc1(x)
x, (hidden, _) = self.lstm_enc2(x)
x = hidden.reshape((batch_size, self.num_layers*self.num_directions, self.num_enc_hidden_dim))
return x
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.device = get_device()
self.num_features = 1 #Features
self.num_seq_length = 180 #Sequence
self.num_directions = 2 #BiDirectional
self.bidirectional = True if self.num_directions > 1 else False
self.num_hidden_states = 2 #LSTM H,C -> GRU H
self.num_hidden_dim = 16
self.num_enc_hidden_dim = 32
self.num_layers = 3 #Layers
#self.dropout = 0.2 #Dropout
self.linear_dims = (self.num_hidden_dim * self.num_directions, 1) #Dimension Linear
self.batch_size = 10
self.lstm_dec1 = nn.LSTM(
input_size=self.num_enc_hidden_dim*self.num_directions*self.num_layers,
hidden_size=self.num_enc_hidden_dim,
num_layers=self.num_layers,
batch_first=True,
bidirectional=self.bidirectional
)
self.lstm_dec2 = nn.LSTM(
input_size=self.num_enc_hidden_dim*self.num_directions,
hidden_size=self.num_hidden_dim,
num_layers=self.num_layers,
batch_first=True,
bidirectional=self.bidirectional
)
self.dense_layer = nn.Linear(self.num_hidden_dim*self.num_directions,self.num_features)
self.lstm_dec1.apply(self.init_weights)
self.lstm_dec2.apply(self.init_weights)
self.dense_layer.apply(self.init_weights)
def init_weights(self, m):
if type(m) == nn.LSTM or type(m) == nn.Linear:
for name, param in m.named_parameters():
if 'bias' in name:
nn.init.constant(param, 0.01)
elif 'weight' in name:
nn.init.xavier_normal(param) #normal?
def forward(self, x):
batch_size = x.shape[0]
x = x.repeat(1, self.num_seq_length, self.num_features)
x = x.reshape((batch_size, self.num_seq_length, self.num_enc_hidden_dim*self.num_directions*self.num_layers))
x, hidden = self.lstm_dec1(x)
x, hidden = self.lstm_dec2(x)
x = x.reshape((batch_size, self.num_seq_length, self.num_hidden_dim*self.num_directions))
x = self.dense_layer(x)
x = x.reshape((batch_size, self.num_features, self.num_seq_length))