Hey all,
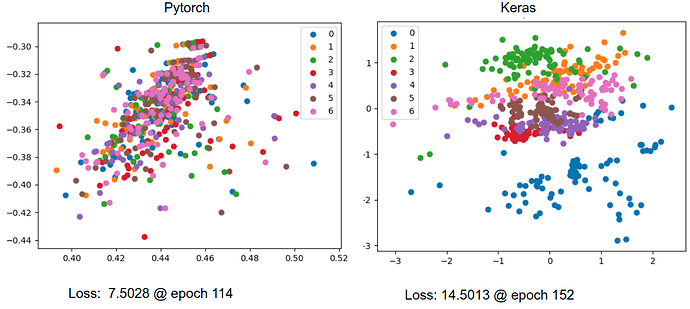
I’m trying to port a vanilla 1d CNN variational autoencoder that I have written in keras into pytorch, but I get very different results (much worse in pytorch), and I’m not sure why. I’ve tried to make everything as similar as possible between the two models. Here is a plot of the latent spaces of test data acquired from the pytorch and keras:
From this one can observe some clustering of the different classes in the keras VAE space but not the pytorch VAE space. t-sne on unprocessed data shows good clustering of the different classes. Interestingly the loss of the pytorch model was lower than the keras model, even though I’ve tried to make the loss functions the same. Plotting reconstructions of data sent through the pytorch model shows that they all look like the average of the data with some variation in the brightness, while the keras model captures much of the variations in the original data. Both show a reasonable trend in loss vs epochs.
I imagine that the problem stems from some difference in implicit settings between keras and pytorch, but I don’t know what the possibilities are. Although its especially strange how different the losses are thoughout training.
Here is my pytorch code:
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, z_dim):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv1d(1, 16, 8, 2, padding=3)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv1d(16, 16, 8, 2, padding=3)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv1d(16, 32, 8, 2, padding=3)
self.conv4 = nn.Conv1d(32, 32, 8, 2, padding=3)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(32*21, 64)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(64, 16)
self.fc21 = nn.Linear(16, z_dim)
self.fc22 = nn.Linear(16, z_dim)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
x = x.view(-1,1,336)
x = self.relu(self.conv1(x))
x = self.relu(self.conv2(x))
x = self.relu(self.conv3(x))
x = self.relu(self.conv4(x))
x = x.view(-1, 672)
x = self.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.dropout(x, 0.3)
x = self.relu(self.fc2(x))
z_loc = self.fc21(x)
z_scale = self.fc22(x)
return z_loc, z_scale
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, z_dim):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(z_dim, 672)
self.conv1 = nn.ConvTranspose1d(32, 32, 8, 2, padding=3)
self.conv2 = nn.ConvTranspose1d(32, 32, 8, 2, padding=3)
self.conv3 = nn.ConvTranspose1d(32, 16, 8, 2, padding=3)
self.conv4 = nn.ConvTranspose1d(16, 16, 8, 2, padding=3)
self.conv5 = nn.ConvTranspose1d(16, 1, 7, 1, padding=3)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, z):
z = self.relu(self.fc1(z))
z = z.view(-1, 32, 21)
z = self.relu(self.conv1(z))
z = self.relu(self.conv2(z))
z = self.relu(self.conv3(z))
z = self.relu(self.conv4(z))
z = self.conv5(z)
recon = torch.sigmoid(z)
return recon
class VAE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, z_dim=2):
super(VAE, self).__init__()
self.encoder = Encoder(z_dim)
self.decoder = Decoder(z_dim)
self.cuda()
self.z_dim = z_dim
def reparameterize(self, z_loc, z_scale):
std = z_scale.mul(0.5).exp_()
epsilon = torch.randn(*z_loc.size()).to(device)
z = z_loc + std * epsilon
return z
vae = VAE()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(vae.parameters(), lr=0.001)
def loss_fn(recon_x, x, z_loc, z_scale):
MSE = F.mse_loss(recon_x, x, size_average=False)*10
KLD = -0.5 * torch.mean(1 + z_scale - z_loc.pow(2) - z_scale.exp())
return MSE + KLD
for epoch in range(1000):
for x, _ in train_dl:
x = x.cuda()
z_loc, z_scale = vae.encoder(x)
z = vae.reparameterize(z_loc, z_scale)
recon = vae.decoder(z)
loss = loss_fn(recon, x, z_loc, z_scale)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
vae.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for i, (x, _) in enumerate(test_dl):
x = x.cuda()
z_loc, z_scale = vae.encoder(x)
z = vae.reparameterize(z_loc, z_scale)
recon = vae.decoder(z)
test_loss = loss_fn(recon, x, z_loc, z_scale)
normalizer_test = len(test_dl.dataset)
total_epoch_loss_test = test_loss / normalizer_test
#my crappy early stopping implementation
if epoch == 0:
loss_test_history = total_epoch_loss_test.item()
patience = 0
else:
loss_test_history = np.append(loss_test_history, total_epoch_loss_test.item())
if total_epoch_loss_test.item() < 0.000001+np.min(loss_test_history):
patience = 0
torch.save(vae.decoder.state_dict(), "~/best_decoder_model.pt")
torch.save(vae.encoder.state_dict(), "~/best_encoder_model.pt")
else:
patience +=1
print(epoch, patience, total_epoch_loss_test.item(), np.min(loss_test_history))
if patience == 32:
break
Here is my keras code:
#conv1dtranspose doesn't exist in keras
def Conv1DTranspose(input_tensor, filters, kernel_size, activation,name, strides=2, padding='same'):
x = Lambda(lambda x: K.expand_dims(x, axis=2))(input_tensor)
x = Conv2DTranspose(filters=filters, kernel_size=(kernel_size, 1), strides=(strides, 1), padding=padding, activation=activation, name=name)(x)
x = Lambda(lambda x: K.squeeze(x, axis=2))(x)
return x
def reparameterize(args):
z_mean, z_log_var = args
batch = K.shape(z_mean)[0]
dim = K.int_shape(z_mean)[1]
epsilon = K.random_normal(shape=(batch, dim))
return z_mean + K.exp(0.5 * z_log_var) * epsilon
latent_dim = 2
inputs = Input(shape=input_shape, name='encoder_input')
x = Conv1D(16, activation='relu', kernel_size=8, strides=2, padding="same")(inputs)
x = Conv1D(16, activation='relu', kernel_size=8, strides=2, padding="same")(x)
x = Conv1D(32, activation='relu', kernel_size=8, strides=2, padding="same")(x)
x = Conv1D(32, activation='relu', kernel_size=8, strides=2, padding="same")(x)
shape = K.int_shape(x)
x = Flatten()(x)
x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x)
x = Dropout(0.3)(x)
x = Dense(16, activation='relu')(x)
z_mean = Dense(latent_dim, name='z_mean')(x)
z_log_var = Dense(latent_dim, name='z_log_var')(x)
z = Lambda(reparameterize, output_shape=(latent_dim,), name='z')([z_mean, z_log_var])
encoder = Model(inputs, [z_mean, z_log_var, z], name='encoder')
latent_inputs = Input(shape=(latent_dim,), name='z_sampling')
x = Dense(shape[1] * shape[2], activation='relu')(latent_inputs)
x = Reshape((shape[1], shape[2]))(x)
x = Conv1DTranspose(x, 32, activation='relu', kernel_size=8, strides=2, name="unconv1", padding="same")
x = Conv1DTranspose(x, 32, activation='relu', kernel_size=8, strides=2, name="unconv2", padding="same")
x = Conv1DTranspose(x, 16, activation='relu', kernel_size=8, strides=2, name="unconv3", padding="same")
x = Conv1DTranspose(x, 16, activation='relu', kernel_size=8, strides=2, name="unconv4", padding="same")
outputs = Conv1DTranspose(x, filters=1,
kernel_size=8,
activation='sigmoid',
padding='same',
strides=1,
name='decoder_output')
decoder = Model(latent_inputs, outputs, name='decoder')
outputs = decoder(encoder(inputs)[2])
vae = Model(inputs, outputs, name='vae')
#I took this loss function for VAEs from one of keras' tutorials. MSE*10 works better than BCE in my experience. I tried to make it the same as in pytorch
reconstruction_loss = mse(K.flatten(inputs), K.flatten(outputs))*10
reconstruction_loss *= original_dim
kl_loss = 1 + z_log_var - K.square(z_mean) - K.exp(z_log_var)
kl_loss = K.sum(kl_loss, axis=-1)
kl_loss *= -0.5
vae_loss = K.mean(reconstruction_loss + kl_loss)
vae.add_loss(vae_loss)
vae.compile(optimizer='adam')
vae.fit(X_train,
shuffle=True,
epochs=epochs,
batch_size=batch_size,
verbose=2,
callbacks=[early_stop],
validation_data=(X_test, None))
Looking at the model summaries of both they look the same (same output shapes and #of parameters), except for the output conv1dtranspose layer in pytorch has to have a kernel size of 7 for the shapes to work (not sure how keras prevents this from happening). I think my optimizer and loss function are the same in both cases. I use a batch size of 32 in both and an early stopping patience of 32 in both.